You can instantiate your Patch Feed, apply the custom ratings to Windows and Linux patches published by the OS vendor using APIs and patch devices against custom rated patches.
You can qualify the patches by providing the following attributes using API:
- Patch rating (Whitelisted, Blacklisted)
- CVE ID (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures identifier)
Available Patch Feed Channels for Windows and Linux
Agent deployed Windows servers can get the missing patches downloaded from
Microsoft cloud through Windows Update Agent (WUA) API or Windows Update Service (WSUS) - Local Repository
Pre-Requisites: Windows
Microsoft Cloud through Windows Update Agent (WUA) API
- Windows Server/Laptop/Desktop should have an OpsRamp Agent installed to perform the patch activities.
- Windows Server should have outbound internet (Proxy or Direct) connectivity to download the patches from the vendor site.
Windows Update Service (WSUS) - Local Repository
- Windows Server/Laptop/Desktop should have an OpsRamp Agent installed to perform patch activities.
- WSUS Services should be enabled on the Windows Server/Laptop/Desktop to download the patches from the local repository.
Agent deployed Linux servers can get the missing patches downloaded from Linux Cloud Public Repository.
Pre-Requisites: Linux
- Linux Public Repos
- Linux Server/Laptop/Desktop should have an OpsRamp Agent installed to perform the patch activities.
- LinuxServer should have outbound internet (Proxy or Direct) connectivity to download the patches from the vendor site.
Installing and Managing the Cloud Patch Feed Integrations
Windows patch feed – Generated from Microsoft authoritative source to contain all the patch data released by Microsoft for different operating system versions.
Linux patch feed – Generated from Linux repositories to contain patch data from different distributions of Linux from all its authoritative sources.
You can install the patch feed for Windows from the Integrations page in the Setup tab.
- Select a client from the All Clients list.
- Go to Setup > Integrations and Apps > + Add.
- On the Available Apps section, click on All Categories and select Patch or click on the search option and type Patch.
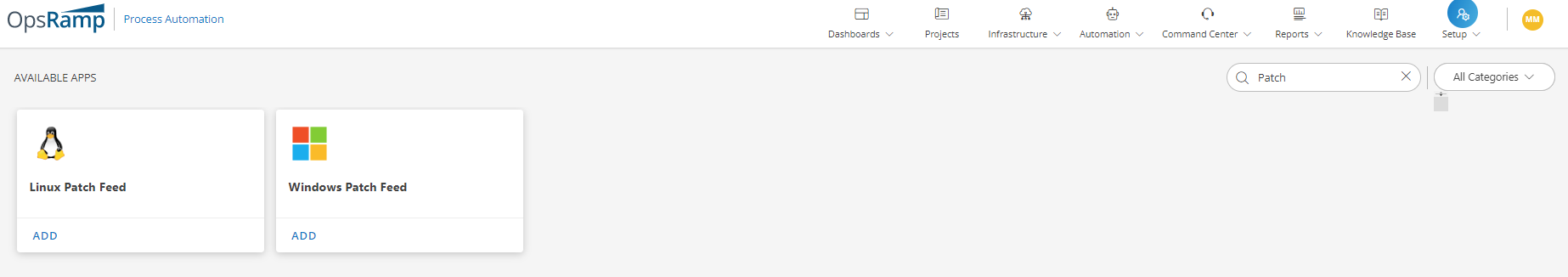
- Click ADD and From PATCH FEED INTEGRATION, click Install.
- From the Install Patch Feed Integration window, provide details for the following parameters:
- Name: Unique name for the patch feed integration.
- Upload Logo: You can browse to upload a logo of your organization.
- Use Service Provider Feed: You can inherit Patch Qualifications and Available Patches details from your Service Provider.
- Click Install.
- From PATCH FEED INTEGRATION, the Authentication section in the API tab displays Authentication Type. The default Authentication Type is OAUTH2.
- Click Save. The Authentication section displays Tenant Id, Key, and Secret. You can use the Key and Secret to generate the authentication token required for API.
Copy the patch feed UID. You can use the patch feed UID while rating the patches for the respective patch feed through API.
- When the client user does not select the Use Partner Feed, the Qualifications section on the Patch Feed Integration page does not display the Patch Rating and corresponding count.
- When the client user unselects the option Use Partner Feed, the ratings of the patches changes to Not Rated and auto-approval of patches reverts to the unapproved, and a new feed for the client is created.
- Patch integration is displayed in My Integrations after installation.
- The rated patches are listed as Whitelisted
For more information on how to create a Patch Feed using API, click the Patch Feed API .
Enabling WSUS Settings on the Server
To have the Windows Servers enabled to download the Missing Patches through WSUS services and Group Policy assigned to the device, follow the below steps.
- Select a Client from All Clients List.
- Go to Infrastructure > Resources > Servers.
- Search for the Resources \ Devices , Select and click on the gear symbol on the top right corner of the page. to disable or enable WSUS Settings.
Once WSUS settings is enabled on the OpsRamp cloud, the agent registry key value should be 1, and these values should be created by the agent.
OpsRamp Internal Path: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\\SOFTWARE\\OpsRamp\\Agent
Key: USE_WSUS
Value: 1Once the above settings are enabled, the agent will look for the following two registry keys, which should not be created by the agent. The customer-side administrator should take care of these registry key as part of the WSUS server configuration.
The WSUS setting is enabled at the device level.
Path: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\\SOFTWARE\\Policies\\Microsoft\\Windows\\WindowsUpdate\\AU key: UseWUServer Value: 1If the WSUS setting is enabled at the device level, the agent will look for the following registry key to locate the WSUS server.
Path: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\\SOFTWARE\\Policies\\Microsoft\\Windows\\WindowsUpdate Key: WUServer Value: http://<your_wsus_server>:8530 Default port: 8530 or 8531
Patch Work Flow Based on the Patch Feed
Vendor Cloud Patch Feed
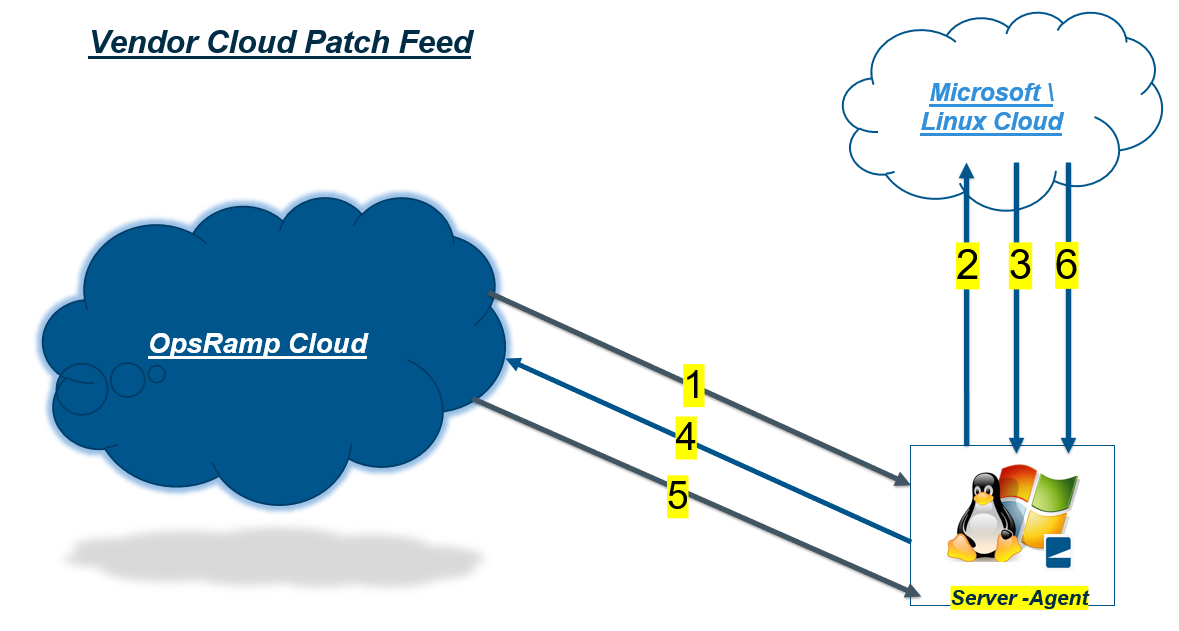
- Step 1: Patch scan request sent from the OpsRamp cloud to the agent deployed Resource/ Device.
- Step 2: Agent enables the Resource \ Device to connect to the Vendor Cloud to queries for the Missing Patch list.
- Step 3 and 4: The Resource \ Device gets the Missing Patch list and reports back to the platform.
- Step 5: Patch installation configuration with Approvals, Reboot Criteria, Automation and Maintenance settings with required selected Patches deployed to the Resources \ Devices.
- Step 6: If the reboot after install flag is selected, the required patches will be downloaded from the cloud, installed by the agent, and then the device will reboot in accordance with the Patch Configurations.
WSUS Patch Feed
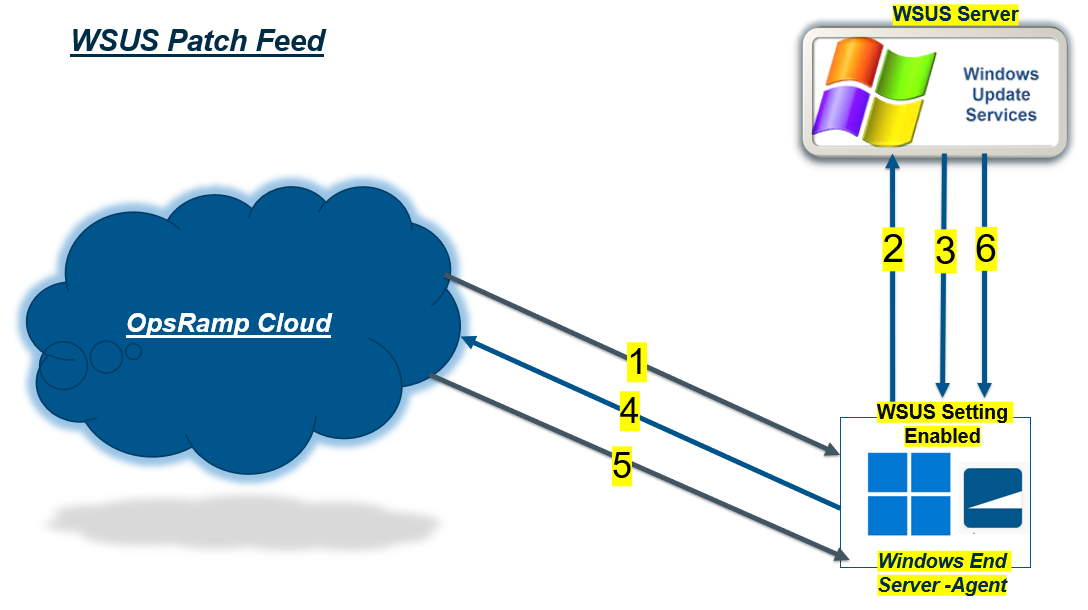
- Step 1: Patch Scan Request sent from the OpsRamp cloud to the agent deployed Resource/ Device.
- Step 2: Agent enables the Resource \ Device to connect to WSUS Server through the Group Policy assigned and queries for the Missing Patch list.
- Step 3 and 4: The Resource \ Device gets the Missing Patch list and reports back to the platform.
- Step 5: Patch Installation configuration with Approvals, Reboot Criteria, Automation and Maintenance settings with required selected Patches deployed to the Resources \ Devices.
- Step 6: If the reboot after install flag is selected, the required patches will be downloaded from the cloud, installed by the agent, and then the device will reboot in accordance with the Patch Configurations.