Introduction
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an application-layer protocol defined by the Internet Architecture Board (IAB) for exchanging management information between network devices. It is a part of the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP⁄IP) suite.
SNMP is one of the widely accepted protocols to manage and monitor network elements. Most of the professional-grade network elements come with bundled SNMP agent. These agents have to be enabled and configured to communicate with the network management system (NMS). The SNMP agent is a program that resides on your managed device, packaged within the network element. You have to enable it on your device. It collects the management information from the device locally and provides it to the SNMP manager. These agents could be standard, for example, Net-SNMP or specific to a vendor, such as HP Insight Agent.
SNMP Credentials
SNMP uses a password-like authorization known as a community string. When you provide an SNMP credential to a device, it checks to see if the community string matches the community string configured on the device. If the string matches, the device responds to the SNMP query.
SNMP Discovery Prerequisites
Classic Gateway
- Allow ICMP between end-device and OpsRamp Gateway.
- Allow UDP port
161/162bi-directional between end-device and OpsRamp Gateway. - Allow SNMP on the end-device.
- Create SNMP credentials and assign them to end-device for discovery.
NextGen Gateway
- Allow ICMP between end device and (nodes, load balancers).
- Allow UDP port
161/162bi-directional between end-device and (nodes, load balancers). - Allow SNMP between end device and (nodes, load balancers).
- Create SNMP credentials and assign them to end-device for discovery.
SNMP discovery attributes against device
As a part of SNMP discovery we are showing below attribute details on the end device:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Basic Information |
|
| More Information |
|
| Hardware Information |
|
| Inventory Tab |
|
| Software Modules |
|
| Interface Tab |
|
Discover the gateway using SNMP
To find the read-only gateway community string, one option is to:
- Log into the gateway WebUI.
- Click SNMP.
Or, you can get the read-only community string by logging into the gateway and reading the string in the /etc/snmp/snmpd.conf file.
You can change the community string to a name of your choice.
Multi-credential functionality
SNMP multi-credential functionality allows you to discover network resources using multiple credentials using a single discovery profile. You can create or use multiple credential sets if you are using a gateway to discover your resources.
For example, a printer uses SNMPv2c credential type and a Cisco router uses SNMPv3 credential type. In such a case, you need to create two discovery profiles. With SNMP multi-credential functionality, you can create one discovery profile and use both the credential sets.
The gateway discovers devices with the credentials, sequentially, as the credentials were entered when a Discovery Profile was created at the time of the first scan. After successful discovery, the gateway remembers resources and their credentials for subsequent discovery.
Multi-credentialed, SNMP-enabled devices have the following advantages:
- Reduces the effort of creating multiple discovery profiles.
- Reduces time for manually traversing through multiple discovery profiles to discover a network resource.
- Scans and discovers a subnet with multiple SNMP community strings.
- Discovers network resources working on different SNMP versions.
SNMP field values
The following provides information on configuring the SNMP fields for creating an SNMP credential set.
SNMPv1 and SNMPv2
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Port | 161 | Agent receives requests on UDP port 161. |
| Community | N/A | Read-only community string. |
SNMPv3
SNMPv3 is a user-based security model. It provides secure access to the devices by combining authenticating and encrypting packets over the network. The security features provided in SNMPv3 are message integrity, authentication, and encryption.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Port | 161 | SNMP Agent port. The default port is 161. |
| Context | N/A | Specify context name (an octet string) that identifies the collection of management information accessible by an SNMP entity. |
| Security Name | N/A | Enter the name of the user (principal) on whose behalf the message is being exchanged. |
| Security Level |
|
|
| Authentication Protocol |
| Authentication in an SNMPv3 uses an encryption algorithm to determine if the data is from a valid source. The encryption algorithms for authentication:
|
| Authentication Password | N/A | Enter the Authentication password. |
| Confirm Password | N/A | Re-enter authentication password for validation. |
| Privacy Protocol |
| Privacy in SNMPv3 uses an encryption algorithm to encode the contents of an SNMPv3 packet. This encoding is used to verify that the content cannot be viewed by unauthorized entities when routed over the network.
|
| Privacy Password | N/A | Enter the privacy password. |
| Confirm Password | N/A | Re-enter authentication password for validation. |
| Connection time-out | N/A - Default value: 10,000 milliseconds | Provide a maximum time period for discovery. If the gateway does not get a response from the device after 10,000 milliseconds, it terminates the discovery. |
Note
Before starting the SNMP-based discovery, the gateway will check for the following ports: 22, 80, 135, 443, 3389, and 5900 on the remote resources to ensure that the resource is available for further discovery.Configure and Install the Integration
From All Clients, select a client.
Go to Setup > Account.
Select the Integrations and Apps tab.
The Installed Integrations page, where all the installed applications are displayed.
Note: If there are no installed applications, it will navigate to the Available Integrations and Apps page.Click + ADD on the Installed Integrations page. The Available Integrations and Apps page displays all the available applications along with the newly created application with the version.
Note: You can even search for the application using the search option available. Also you can use the All Categories option to search.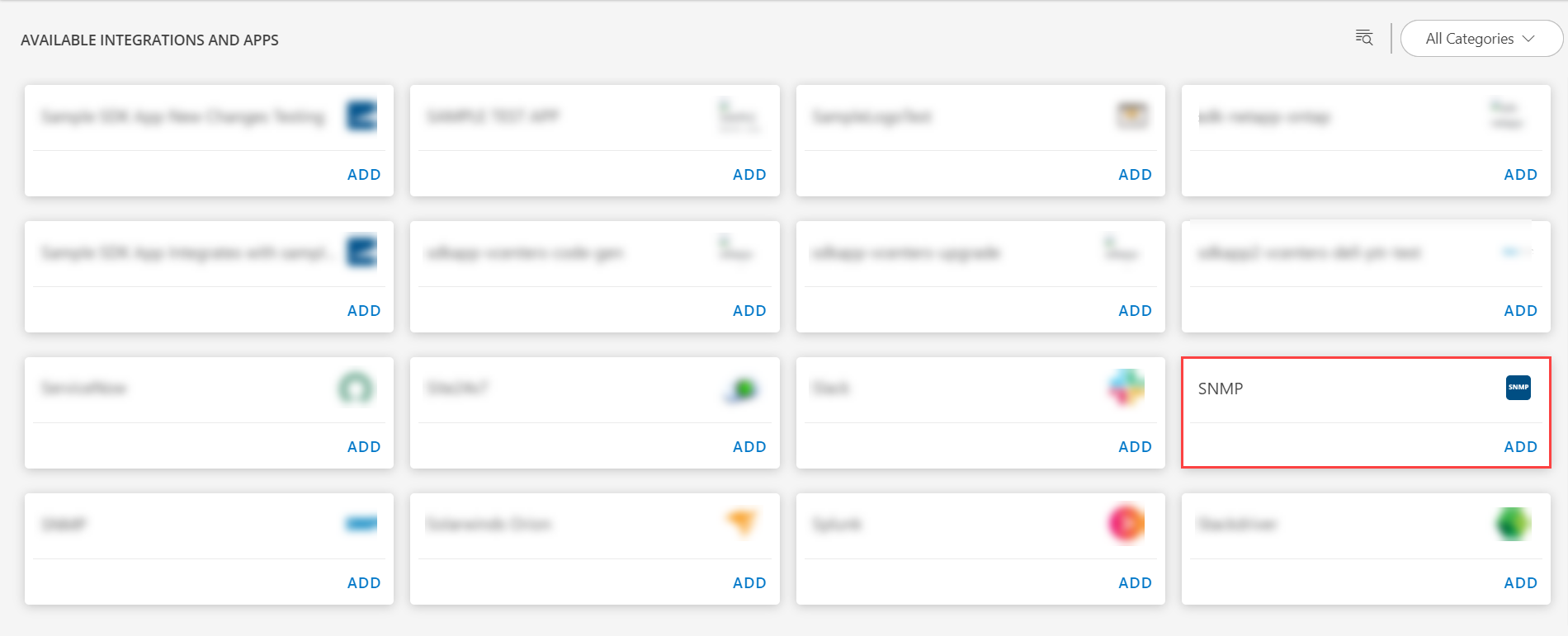
Click ADD on the SNMP tile.
From the Configurations page, click + ADD.
Enter the below mentioned BASIC INFORMATION:
Name: Enter the name for the integration.
Profile Type (Note: We support Cisco and Aruba WLAN Controllers only): Select any Profile Type.
Note: Based on the profile type selected, the fields for input change.

Credentials: Select a credential from the drop-down list. This credential refers to the access, authorization, or authentication credentials assigned to your devices managed by the network administrators.
- (Optional) Click + Add to create a credential. The ADD CREDENTIAL window is displayed. Enter the following information.
- Name: Credential name.
- Description: Brief description of the credential.
- SNMP Version: Select a version. Default is V1. Click here for more information.
- Port: Enter the port. Default is 161. Click here for more information.
- Community: Enter the community string. Default is public. Click here for more information.
- Connection Timeout(ms): Specify the connection timeout in milliseconds. Click here for more information.
- (Optional) Click + Add to create a credential. The ADD CREDENTIAL window is displayed. Enter the following information.
CLI Credentials: Select a credential from the drop-down list. This credentials refer to the Command Line Interface credentials used to remotely log in to a network device via SSH or Telnet to retrieve additional device configuration
(Optional) Click + Add to create a credential. The ADD CREDENTIAL window is displayed. Enter the following information.
Discovery Type: Select the discovery type from the list:
- IP Range: Select this option if you have an IP range and enter all the IP addresses in the box separated by a comma, or enter a range of IP addresses to be discovered.Note:Ensure not to add duplicate IP addresses to the IP Range filed in the discovery profile. Duplicate entries can prevent the application from saving the corresponding resource to the database.
The IPRange field supports subnet masks of /20 or smaller. Larger subnets (For example, /16, /15, and so on) are not supported. - Exclude IP Range:Select this option if you want to exclude specific IPs from the provided IP Range field. It supports comma-separated individual IPs, subnets, and IP ranges.
When the Exclude IPs option is used, the tool automatically removes the network and broadcast addresses from any subnets specified in the IP range field.
Note: Applicable from 19.1.0 GW release. - Discover only SNMP enabled devices: If we enabled this flag then OpsRamp application will discover only SNMP responding devices.
- Use CDP, LLDP: If enabled, the application will collect neighbourhood information from Layer two protocols (CDP and LLDP).
- Use OSPF, BGP, BRIDGE: If enabled the application will collect neighbourhood information from three Layer protocols (OSPF, BGP and BRIDGE).
- Use LOAD BALANCER: If enabled, the discovered device type is load balancer and the application will collect additional info.
- Use reverse DNS lookup: If enabled, the application will get the DNS name of the device.
- Discover VoIP phones: If enabled, and if the discovered devices are voip devices then the application will collect additional info.
- Advanced Options: Two options are displayed when you select advanced options.
- Use CDP, LLDP: If enabled, the application will collect neighbourhood information from Layer two protocols (CDP and LLDP).
- Use OSPF, BGP, BRIDGE: If enabled the application will collect neighbourhood information from three Layer protocols (OSPF, BGP and BRIDGE).
- Use LOAD BALANCER: If enabled, the discovered device type is load balancer and the application will collect additional info.
- Use reverse DNS lookup: If enabled, the application will get the dns name of the device.
- Discover VoIP phones: If enabled, and if the discovered devices are voip devices then the application will collect additional info.
- Advanced Options: Two options are displayed when you select advanced options.
- TCP Ports for Host Discovery: The OpsRamp tool does the port scan for the mentioned TCP port(s).
Specify ports as a comma-separated list. If no port is specified, ports 80 and 443 are used by default. - Perform SNMP scan against discovered host: If you select this option, OpsRamp performs NMAP discovery first, followed by SNMP discovery for devices that respond to NMAP.
If you do not select this option, NMAP discovery is skipped, and SNMP discovery is performed directly. - Packets to send per second for the scan: Select a desired packet rate from the dropdown.
- Default: Select default to let the OpsRamp tool automatically adjust packet transmission rate during device reachability scans based on available network bandwidth.
- Select a specific value from the list of values
(100, 200, 300, 400, and 500) to manually control the rate. Note: The Packet Count feature is supported only from Gateway version 19.2.0 onwards.
- TCP Ports for Host Discovery: The OpsRamp tool does the port scan for the mentioned TCP port(s).
- IP Range: Select this option if you have an IP range and enter all the IP addresses in the box separated by a comma, or enter a range of IP addresses to be discovered.Note:Ensure not to add duplicate IP addresses to the IP Range filed in the discovery profile. Duplicate entries can prevent the application from saving the corresponding resource to the database.
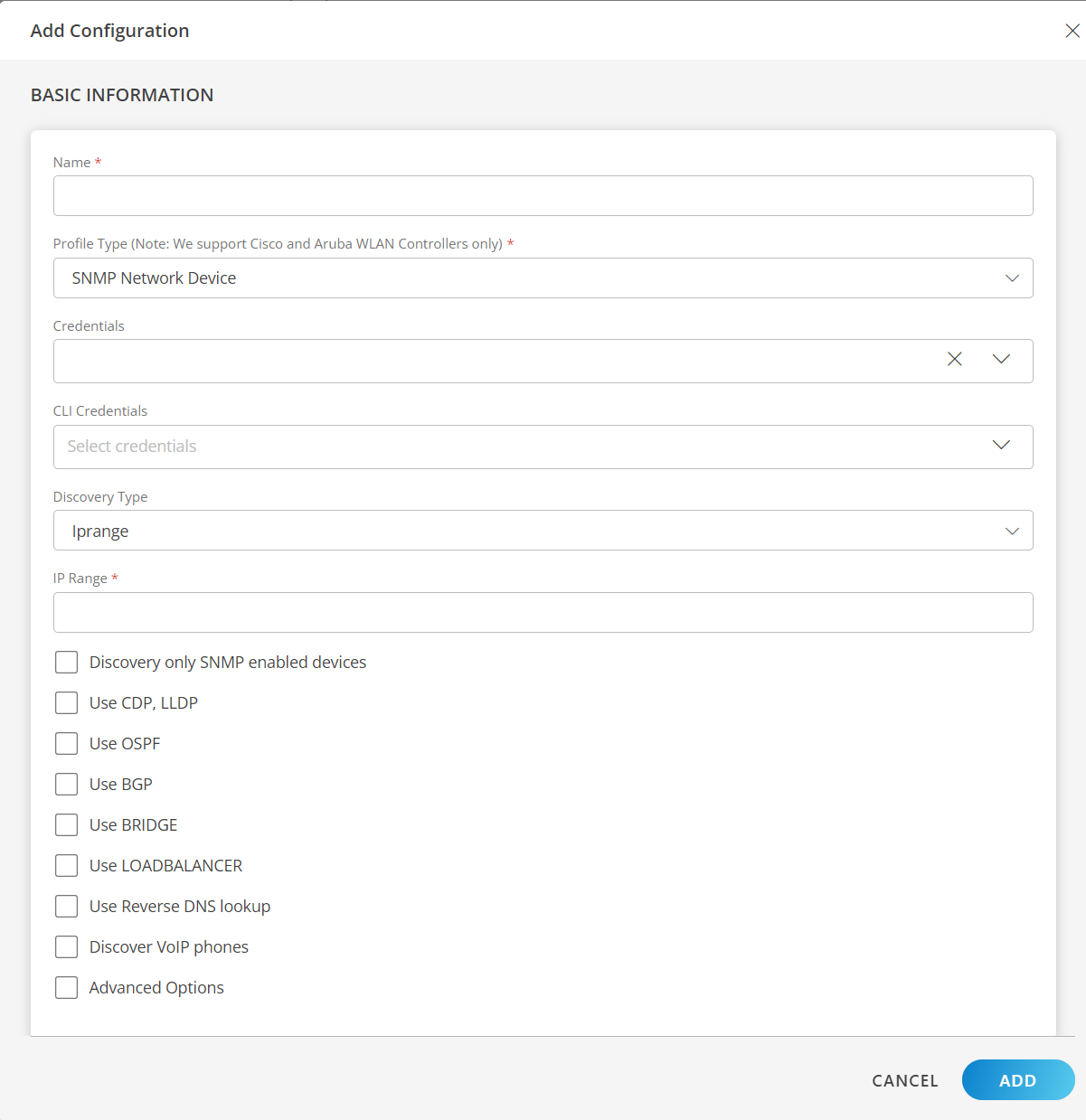
- Seed: Enter the IP address of the root or the seed device. Seed IP defines the range of IP addresses where network discovery starts a scan. When a seed IP is defined, the root device and the adjacent neighbors of the root device are scanned.
- Depth: Select the depth from the drop-down list. The devices are scanned at a depth starting from the IP of the root device. Depth defines the level of the network you want to scan. Example: Depth 1 indicates the seed or the root device and its immediate neighbors. Depth 2 indicates seed or the root device including its immediate neighbors and their immediate neighbors.
- Seed IPs: Enter the IP address of the root or the seed device. Seed IP defines the range of IP addresses where network discovery starts a scan. When a seed IP is defined, the root device and the adjacent neighbors of the root device are scanned.
- Include Subnet: Select this option if you want to discover devices of a specific subnet. To discover a specific subnet in the Seed IP, enter the subnet IP in CIDR format. Example: You want to discover devices from IPs 172.24.22.0 to 172.24.22.255 in a subnet, provide IP in CIDR format as 172.24.22.0/24.
- Exclude Subnet: Select this option if you want to discover devices excluding those of a specific subnet. To exclude discovery of a specific subnet in the Seed IP, enter the subnet IP in CIDR format. Example, you want to exclude IPs 172.24.22.0 to 172.24.22.255 in a subnet, provide IP in CIDR format as 172.24.22.0/24.
SNMP Network Device
If you select SNMP Network Device as profile type, provide inputs for the following fields:
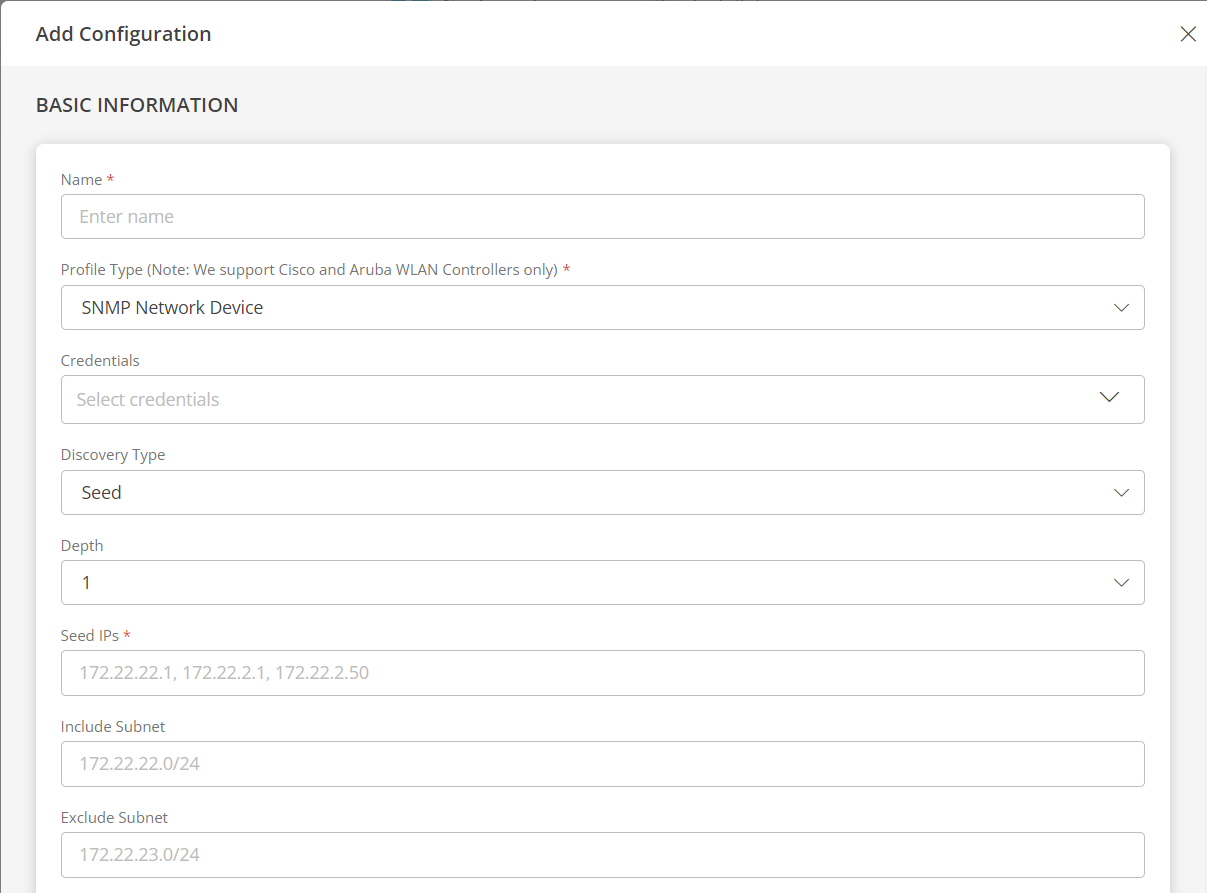
- Credentials: Select a credential from the drop-down list. This credential refers to the access, authorization, or authentication credentials assigned to your devices managed by the network administrators.
- (Optional) Click + Add to create a credential. The ADD CREDENTIAL window is displayed. Enter the following information.
- Name: Credential name.
- Description: Brief description of the credential.
- SNMP Version: Select a version. Default is V1. Click here for more information.
- Port: Enter the port. Default is 161. Click here for more information.
- Community: Enter the community string. Default is public. Click here for more information.
- Connection Timeout(ms): Specify the connection timeout in milliseconds. Click here for more information.
- IP Address: Enter the IP address.
- Monitor Access Points: Select this checkbox, if you want to monitor the access points. Select the frequency (in minutes). The access points monitoring data for the selected frequency will be displayed on the device details page.
- (Optional) Click + Add to create a credential. The ADD CREDENTIAL window is displayed. Enter the following information.
WLAN AP
If you selected WLAN AP as profile type, provide inputs for the following fields:
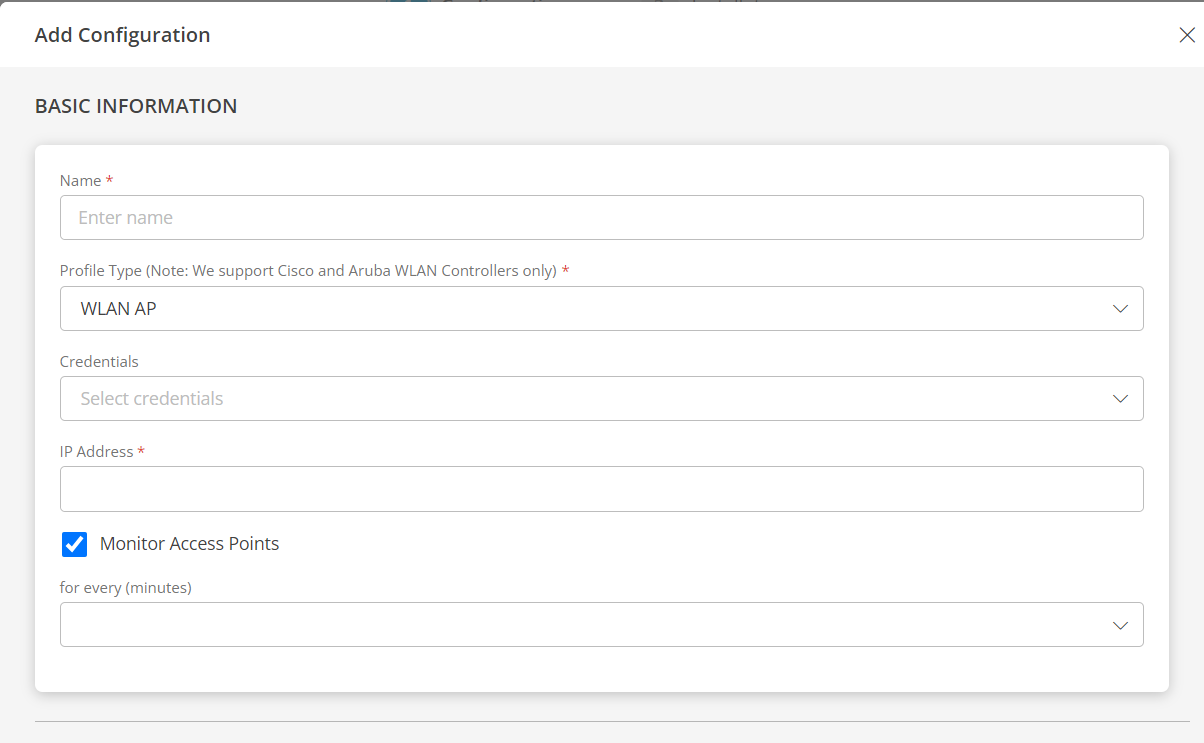
- Credentials: Select a credential from the drop-down list. This credential refers to the access, authorization, or authentication credentials assigned to your devices managed by the network administrators.
- (Optional) Click + Add to create a credential. The ADD CREDENTIAL window is displayed. Enter the following information.
- Name: Credential name.
- Description: Brief description of the credential.
- SNMP Version: Select a version. Default is V1. Click here for more information.
- Port: Enter the port. Default is 161. Click here for more information.
- Community: Enter the community string. Default is public. Click here for more information.
- Connection Timeout(ms): Specify the connection timeout in milliseconds. Click here for more information.
- IP Address: Enter the IP address.
- (Optional) Click + Add to create a credential. The ADD CREDENTIAL window is displayed. Enter the following information.
WLAN Controller
If you selected WLAN Controller as profile type, provide inputs for the following fields:
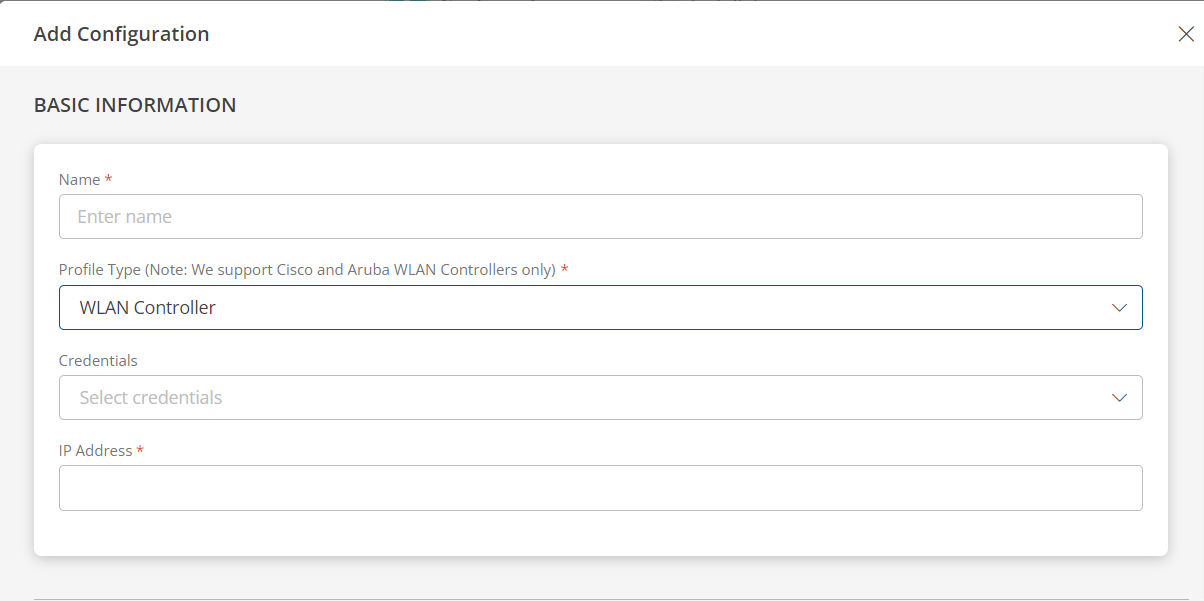
Note
Choosing WLAN Controller as the profile type during WLAN Controller discovery activates the additional Thin Access Points tab on the WLAN Controller device level, which provides details about the access points connected to the controller.- From the PERFORM ACTIONS section, choose Manage Device to set the resources as managed.
- From the FILTER BY QUERY, click + QUERY and select the Attributes, Operator, or use </> to enter the Input query.
- In the DISCOVERY SCHEDULE section, select recurrence pattern to add one of the following patterns:
- Minutes
- Hourly
- Daily
- Weekly
- Monthly
- Click ADD.
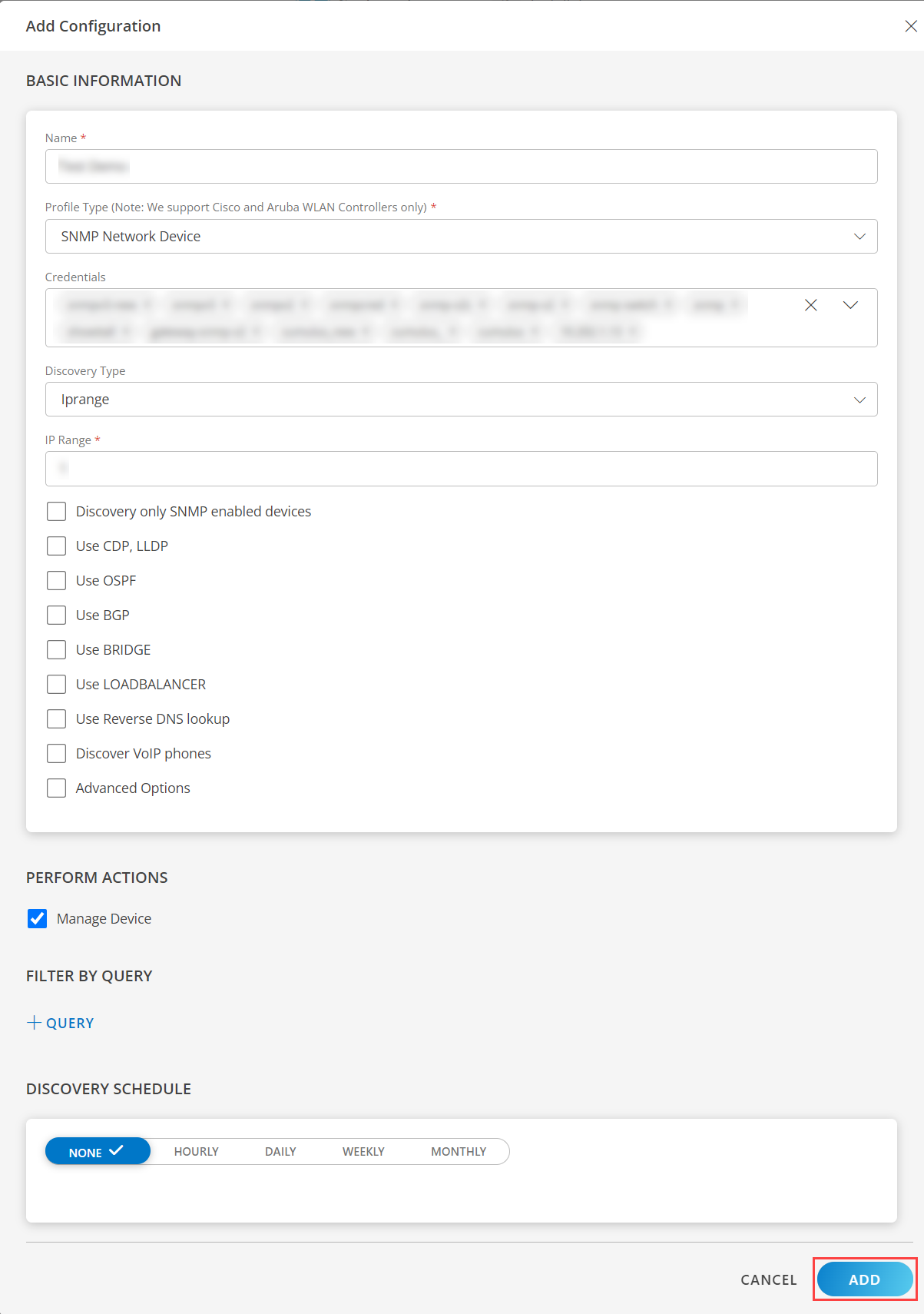
Now the configuration is saved and displayed on the configurations page after you save it. Note: From the same page, you may Edit and Remove the created configuration.
- Click NEXT.
- (Optional) Click +ADD to create a new collector by providing a name or use the pre-populated name.
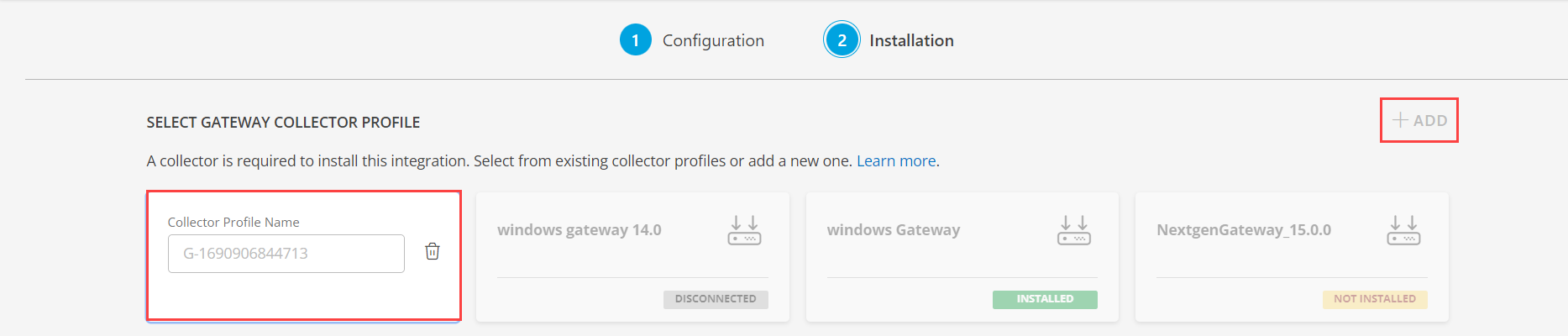
- Select an existing registered profile.
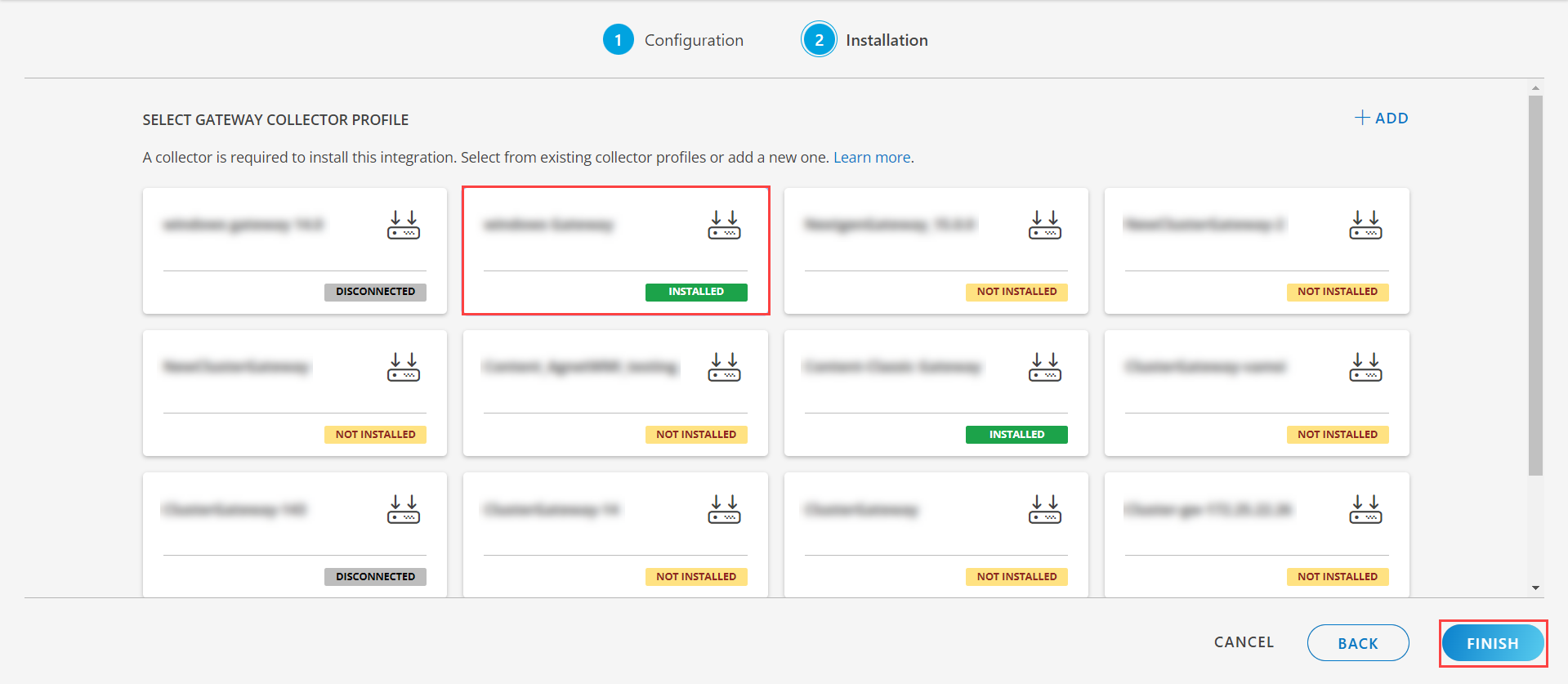
- Click FINISH.
The application is now installed and displayed on the Installed Integration page. Use the search field to find the installed application.
Note: By default, the Discovery Status is displayed as Completed, for recurring schedules, but actual discovery scan will start at the scheduled time. The Discovery scheduling is updated in the Gateway when configuration is saved.
Modify the Installed Integration
See Modify an Installed Integration or Application article.
Note: Select the SNMP application.
SNMP Definition Requests
You can view and submit SNMP definitions for review.
Only Service Provider (SP) and partner-level users can submit SNMP definition requests. All user levels, including SP, partner, and client, can view existing definitions.
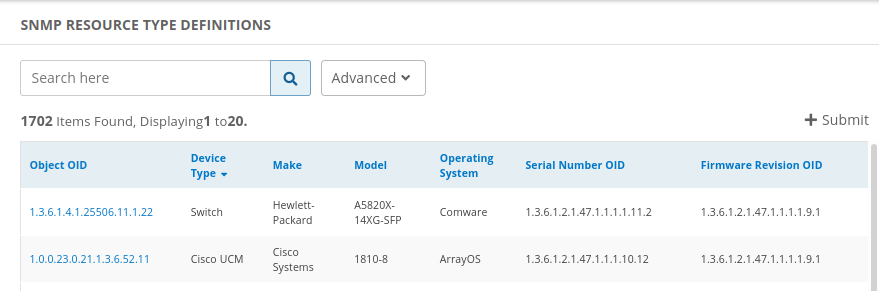
View SNMP definition requests
- Go to Setup > Resources.
- Click SNMP Device Type Definitions. This displays the list of available definitions, as shown in the example:
Submit SNMP definition request
Go to Setup > Resources.
Click SNMP Device Type Definitions.
Click the +Submit button.
In the Add SNMP Device Type Definition page, enter the following information:
Device Type Definition:
Field Required Description Object OID Yes Object identifier. Make Yes Choose the make from the drop-down list. Model No If you selected Model, choose the model from the drop-down list. Model OID No If you selected Model OID, enter a model identifier. Device Type Yes Choose a device type from the drop-down list. Operating System Yes Choose an operating system from the drop-down list. Serial Number OID No Serial number identifier. Firmware Revision OID No Firmware revision identifier. Hardware Revision OID No Hardware revision identifier. Software Revision OID No Software revision identifier. SNMP OIDs for Network Interface Information:
Field Required Number of Interfaces No Name No Alias No Index No Type No Speed No Operational Status No Admin Status No Click Cancel to discard your definition or click Submit, which displays the following advisory message:
This definition will reflect on devices only after it is reviewed by a vistara admin. You can check the status on the definition listing page.Click Yes to continue and submit your definition for review.
SNMP Discovery Troubleshooting Steps
Unable to see the discovered devices under discovery profiles?
Device should be enabled with SNMP protocol or device should be reachable from the gateway
How to check the device reachable?
Command
ping <ipaddress>If the device is enabled with SNMP, then make sure whether the device responds to SNMP.
- SNMP version 1:
Basic Syntax
snmpwalk -v1 -c <community> <ipaddress> <OID>- Example: snmpwalk -v1 -c community 10.10.10.10 1.3.6.1.2.1.1
- SNMP version 2:
Basic Syntax
snmpwalk -v2c -c <community> <ipaddress> <OID>- Example: snmpwalk -v2c -c community 10.10.10.10 1.3.6.1.2.1.1
- SNMP version 3:
Basic Syntax
snmpwalk -v3 -l <noAuthNoPriv|authNoPriv|authPriv> -u <username> -a <MD5|SHA> -A <MD5|SHA key> -x <DES|AES> -X <DES|AES key> -n <context> <ipaddress> <OID>- Example: snmpwalk -v3 -l authPriv -u user4 -a MD5 -A 1234567890abcdef -x DES -X 1234567890abcdef 10.197.1.1 1.3.6.1.2.1.1
Unable to see the discovered devices under discovery profiles even snmp is working?
- If the SNMPwalk command is functioning correctly, it is essential to verify the SNMPget command as well. This is crucial as we rely on the SNMPget command to retrieve information from the Netscaler.
Basic Syntax
snmpget -v2c -c <community> <ipaddress>- Example: snmpget -v2c -c Ac-5nmp! 192.168.147.26 1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0
If SNMPwalk is operational but the SNMPget command is not functioning, resulting in request timeouts, credentials cannot be obtained. Without valid credentials, device discovery using SNMP becomes impossible. Therefore, it is imperative to ensure the functionality of both commands.
If the device responds to SNMP, it is crucial to confirm that the SNMP credentials utilized align with those assigned in the discovery profile. The SNMP credentials eliciting a response from the device should precisely match the credentials specified in the SNMP discovery profile.
Ensure that the correct gateway selected in the discovery profile is being utilized.
If SNMPv3 credentials are in use and a context name is specified in the credentials, it is important to note that when checking SNMPwalk or SNMPget commands from the gateway, the context name must be explicitly included in the command. In the event of a request timeout, it is advised to remove the context name from the credentials and initiate a re-discovery process.
Syntax
snmpwalk -v3 -l <noAuthNoPriv|authNoPriv|authPriv> -u <username> -a <MD5|SHA> -A <MD5|SHA key> -x <DES|AES> -X <DES|AES key> -n <context> <ipaddress> <OID>- Note:In general context is used to differentiate multiple instances managed by the SNMP Agent.
If device is reachable from the gateway as well as device is also responding with SNMP but still unable to see the discovered devices.
Need to check the vprobe logs in the gateway. The vprobe logs is saved in
/var/log/app/vprobe.log.Issue the following command to check the ongoing discovery logs.
tail -f /var/log/app/vprobe.logPerform SNMP discovery again and observe the logs.
logs analyzation:
- SNMP started: Snmp4JSessionImpl#63: Snmp session intialized
- AbstractNetworkDiscovery#62: ************ Discovery scan started for profile 3008 ************
- Device not reachable from gateway: NetworkDiscoveryResponseListenerImpl#114: Resource failed to discover V4:172.26.1.16, sourceNMAP
- Device SNMP credential timeout: SnmpResourceDiscoveryImpl#82: Snmp time out : V4:172.26.1.14
- Device discovery failed with SNMP: NetworkDiscoveryResponseListenerImpl#114: Resource failed to discover V4:172.26.1.14, sourceSNMP
- Discovery is completed: Snmp4JSessionImpl#83: Snmp session disconnected.
If no conclusive information is found, consider enabling additional debug logs for a more detailed analysis.
How to enable more debug logs?
Connect to gcli
vgprompt#gcli + enterEnter following command
gcli@gateway>nd log on <30 no of mins>Example: gcli@gateway>nd log on 30
ntwrk.disc on A Timer with timeout 30min has created to revert the val to off
snmp.disc on A Timer with timeout 30min has created to revert the val to off
snmp.topology on A Timer with timeout 30min has created to revert the val to off
disc.response on A Timer with timeout 30min has created to revert the val to off
gcli@gateway>Perform the discovery process again after executing the following command.
tail -f /var/log/app/vprobe.log
After the completion of the discovery process, analyze the vProbe logs as indicated in the previous comments.
logs analyzation:
- Device snmp timeout: com.vistara.gateway.plugin.discovery.error.snmp.SnmpTimeOutException: Snmp is not working with any credential for device :V4:172.26.1.14
- Successfully discovered devices json files: AbstractDiscoveryResponseSerializer#39: Response is saved to /var/log/app/tmp/network-discovery-chunk-1559559930044.json
- Notes:
- Upon discovery, devices will transmit their information to the cloud, and this data is logged in files. Kindly review the log files located in the /var/log/app/tmp/ directory for further details.
- File name start from network-discovery-chunk-
.json - To view the timestamps of the most recent files, execute the following commands:
cd /var/log/app/tmp/ folder
ll network-discovery-chunk-*.json
Discovered devices data is not matching with actual device data like device type,os,etc..
Improper/wrong device data can be possible in following case:
- Check /var/log/app/tmp/network-discovery-chunk-<1559559930044>.json files whether device data is correct or not.
- Check /var/log/app/tmp/network-discovery-chunk-<1559559930044>.json files whether device data is correct or not.
If the data is incompatible with the fields in SNMP device type definitions within the UI, the device data may become inconsistent. In such cases, navigate to the corresponding Management Profile, synchronize SNMP Device Type Definitions. This action will push the SNMP device type definitions back to the respective gateway. Subsequently, initiate a rescan of the SNMP Discovery Profile to ensure that the changes are reflected in the device.
How to capture SNMP packets on specific device?
Execute the following command at gateway and perform the discovery
Command
tcpdump -v -i any 'ip host <ip> && udp port <port>' -s 3000 -w /home/ruser/{filename}.pcapTo stop the above command press ‘ctrl + enter’
Above command can be used to check the device behavior while discovery is going on. As well as we can analyze the collected data.
You may read the tcpdump generated file with help of wireshark tool.
Although the credentials work for the devices during a manual walk, the V3 credential devices are not being discovered in OpsRamp; only one device is discovered out of all of them
- For V3 credentials, the contextEngineID of the same model devices causes this issue. We need to check the contextEngineID of the devices. If it is same, need to check with the vendor.
- ContextEngineID: The contextEngineID is a key concept in the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), particularly in SNMP version 3 (SNMPv3). It uniquely identifies an SNMP engine within an administrative domain. This identifier is crucial for accessing and managing information in different contexts within the SNMP framework.
- How to retrieve the contextEngineID in SNMPv3? You can use the snmpget command. Syntax: snmpget -v 3 -u -l authPriv -a -A -x -X 1.3.6.1.6.3.10.2.1.1.0
SNMP Troubleshooting steps in Nextgen Gateway
How to enable flags in gcli and view vprobe logs in nextgen-gateway?
- Login to the gateway CLI
- Execute command kubectl exec -it nextgen-gw-0 -c vprobe -n <namespace> – bash
Note: Here we need to replace the <namespace> if applicable, otherwise execute kubectl exec -it nextgen-gw-0 -c vprobe – bash - To enable flags by using this command gcli nd log on 30
- To exit the gcli, enter the “exit” command.
- To view the logs, execute tail -100f /var/log/app/vprobe.log
- Within the directory /var/log/app, you will find the logs generated by vprobe. For discovery chunk files and topology JSON files, navigate to the /var/log/app/tmp folder. These files are in the format of “network-discovery-chunk-xyz.json” and “network-topology-xyz.json”.
- To copy files from the vprobe container to the gateway cli, execute the following command after exiting the container
kubectl cp <namespace>/nextgen-gw-0:<source_path> <dest_path> -c vprobe
Example:kubectl cp nextgen-gw-0:/var/log/app/vprobe.log /home/gateway-admin/vprobe.log -c vprobe - Download files from the Gateway CLI.
For discovery trouble shooting, perform SNMP Discovery troubleshooting steps using above mentioned nextgen-gateway steps.
SNMP Version History
| Application Version | Bug fixes / Enhancements |
|---|---|
| 19.1.0 | Added support for retrieving physical component and software module information for Juniper devices using Juniper-specific MIB OIDs when generic Entity MIB OIDs are unavailable during SNMP discovery. |
Added support to display the ifMtu attribute value in the network card details for SNMP discovered resources. | |
| Added Exclude IPs option support for SSH, SNMP, and WMI discoveries. | |
| Fixed an issue preventing the SNMP app's View Logs from displaying over 2,000 device discovery entries. | |
| 18.2.0 | Added support for detailed discovery activity information in SNMP, Linux, and WMI discoveries, including the number of reachable devices and the count of successful SNMP, WMI, or SSH connections. |
| 18.1.0 | Added support for visualizing BGP and OSPF links within the network topology. |
| Added support to exclude broadcast IPs from discovery within the specified subnet. | |
| 18.0.0 | Implemented a fix to allow SNMP discovery to proceed even if component OIDs fail to respond on the end device. |
| Added a fix to retrieve BGP Neighbors using the getNext operation during SNMP discovery. | |
| 15.1.0 | Addressed an issue to ensure RAM attribute values are correctly displayed for devices discovered via SNMP. |
| 14.0.0 | SNMP v3 credential support now includes AES-192-C and AES-256-C privacy protocols. From Gateway version 14.0.0, you can discover and monitor devices using these protocols by enabling them while creating SNMP credentials in OpsRamp. |